
These days, it’s rare to find a business of any size and in any industry that isn’t considering what analytics and business intelligence can do for them. That includes utilities, of course. Like any other business, utilities gather increasing volumes of data about their customers, so it’s natural to wonder how that data might be best put to work.
Data analytics isn’t really new, but the types and capabilities that analytics brings has definitely changed over time. The level of analytic maturity of most businesses, though, has a ways to go to catch up to the current state of the scientific art. This is especially true in industries like utilities which, for a variety of reasons, are slow to adopt new technologies. But whether a company is a slow or fast adopter, now more than ever, they need the capabilities more mature analytics offer. This may be purely for optimizing operational efficiency. It may be to retain customers or provide the next level of customer service and customer experience. For utilities in deregulated areas, it may be the key to staying competitive.
Let’s take a look at how analytics have evolved, and why evolving right along with them is so important to today’s utilities.
The four stages of analytics maturity
The Gartner Analytics Ascendency Model has been around since 2012 and is still one of the most common ways of describing and assessing a business’ level of analytics maturity. In a nutshell, it describes how, as a company’s analytics capabilities progress from one level to the next, the great the potential value can be derived from the data.
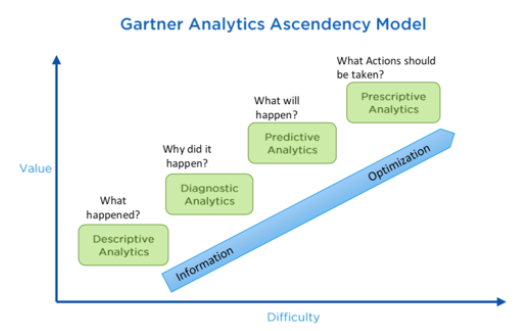
According to this model, the four stages of analytics maturity are, from lowest to highest:
- Descriptive analytics – What happened?
- Diagnostic analytics – Why did it happen?
- Predictive analytics – What will happen?
- Prescriptive analytics – What should you do when it does? (what action to take)
As you might imagine from the insights each type provides, the maturity level is also an indicator of the level’s difficulty, the computational power required, and (not surprisingly) the prevalence of companies at each level.
Data science, machine learning, and predictive analytics
Analytics is sometimes used interchangeably with business intelligence, but that’s only half the story. Represented by levels 1 and 2 in the maturity model, descriptive and diagnostic analytics have been around for some time. Analyzing data to answer what happened isn’t that mysterious, and nor is determining why it occurred. When it comes to predicting what will happen and doing something about it, data science comes into play, and things gets interesting.
This is where more mature analytics capabilities apply machine learning. Machine learning is the use of statistical techniques to:
- Give computer systems the ability to progressively improve performance on a specific task with data, without being explicitly programmed; and
- Devise complex algorithms that enable predictions to produce reliable, repeatable decisions and results and uncover hidden insights
The words and phrases I’ve highlighted above are important. That’s because the new abilities that machine learning enable are driven forward by the veritable explosion and availability of massive computational power and all that data we’ve been collecting for years. Without these, we could not develop and utilize self-learning algorithms that can automatically predict the likelihood of future behaviors (of customers, for example) and even recommend or automate the actions to be taken to ensure or prevent such outcomes. These two, respectively, are predictive and prescriptive analytics. The algorithms that make such insights, decisions, and actions possible have the ability to constantly learn from historical relationships and trends in the data from myriad sources.
Numerous examples exist in the world around us and are so commonplace they’re almost taken for granted, and tomorrow’s applications are already on the drawing board. For example, the navigation apps in our cars and phones automatically provide alternate routes based on up-to-the-minute traffic and roadway conditions. Your favorite ride share adapts its rates based on supply and demand (surge pricing). Credit card companies automate fraud detection and take action to prevent it. Speech and image recognition algorithms are constantly learning and improving themselves. Tomorrow, we’ll see automated countermeasures for cyberattacks, self-driving cars, critical medical diagnoses and treatments based on the human genome, and smart robots.
But why do utilities need advanced analytics?
As you can see, mature analytics has an unlimited number of applications that do and will affect our lives. But as great as all these examples are in these respective fields, how can increasing a utility’s analytic maturity help it meet its business imperatives? Here are just a few use cases, which we’ll explore in more depth in future articles.
|
Network performance, safety, and reliability
|
|
|
Customer engagement
|
|
|
Revenue management
|
|
|
Demand/supply management
|
|
|
Operational efficiency |
|
It’s time for utilities to move beyond the “what” and “why” insights from their data, to predicting what will happen next and taking the appropriate actions to a beneficial outcome for both the utility and customer. The VertexOne Analytics Engagement Model provides a range of analytics services and capabilities to help any utility increase its analytic maturity.





