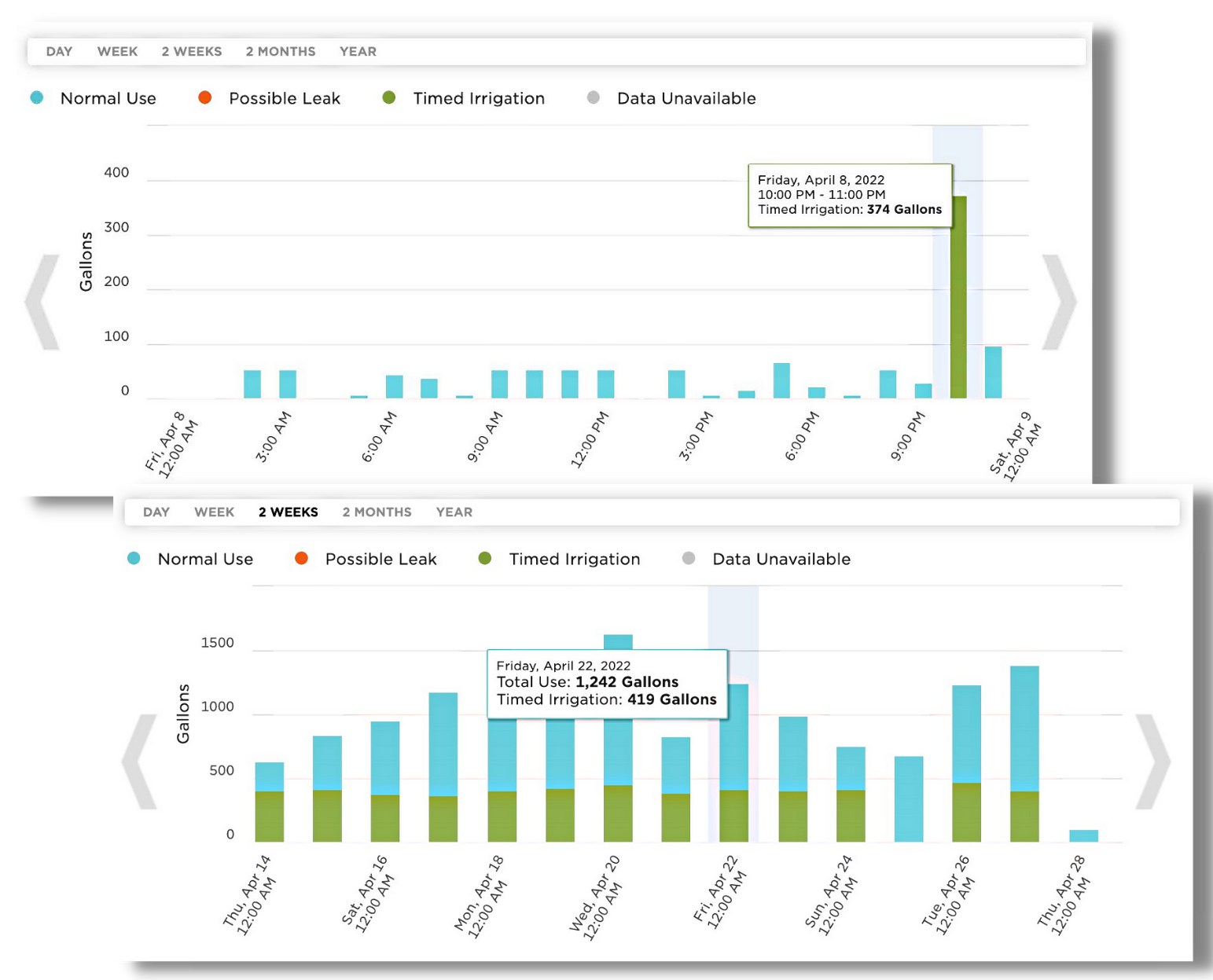
According to the EPA, as much as 50% of water used for irrigation is wasted due to inefficient watering methods and systems.
Luckily, behavioral intervention can be effective in promoting customer engagement and water conservation through AMI portals, provided they are applied and evaluated consistently. Give customers a unified digital experience across all meter types, and drive conservation and compliance with watering restrictions so your team so your team can focus on more complex duties.
Buda, Texas is 15 miles south of downtown Austin, along IH-35. The town has experienced rapid population growth over the last two decades, with population increases from 2,400 to roughly 15,000 residents in 2022. Buda's water sources include Edwards Aquifer Canyon Lake (GBRA) and Alliance Water (Carrizo Aquifer).
Buda installed Automatic Meter Reading (AMR) in 2007, but the surging growth combined with changing environmental and regulatory conditions made it clear that changes had to occur.
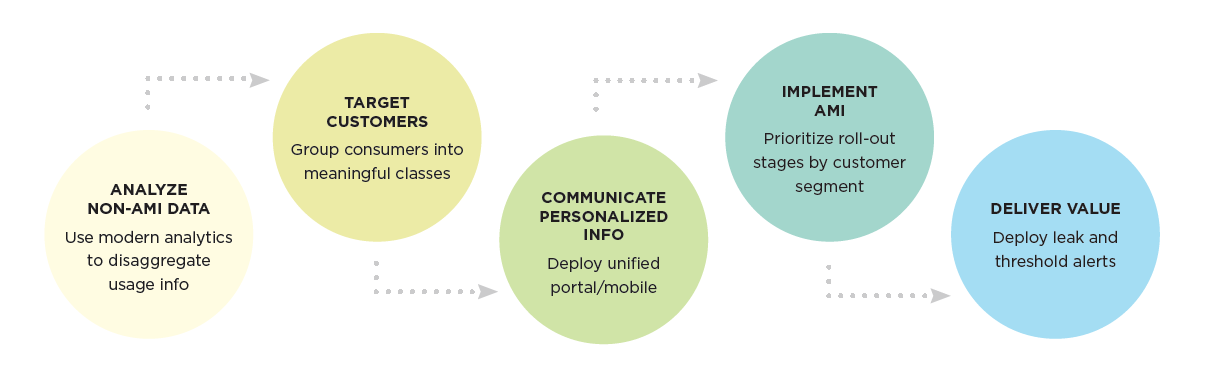
Many of the common benefits that are touted by AMI vendors are now available to non-AMI utilities. By combining multiple data sources with modern analytics technologies, utilities and end-users can glean many useful insights into water use patterns.
As AMI meters are deployed, interval data can be immediately made available to customers via mobile and web interfaces. This allows for a staged deployment that provides real-time water use information, leak alerts, and highly accurate household water use disaggregation detail to consumers.